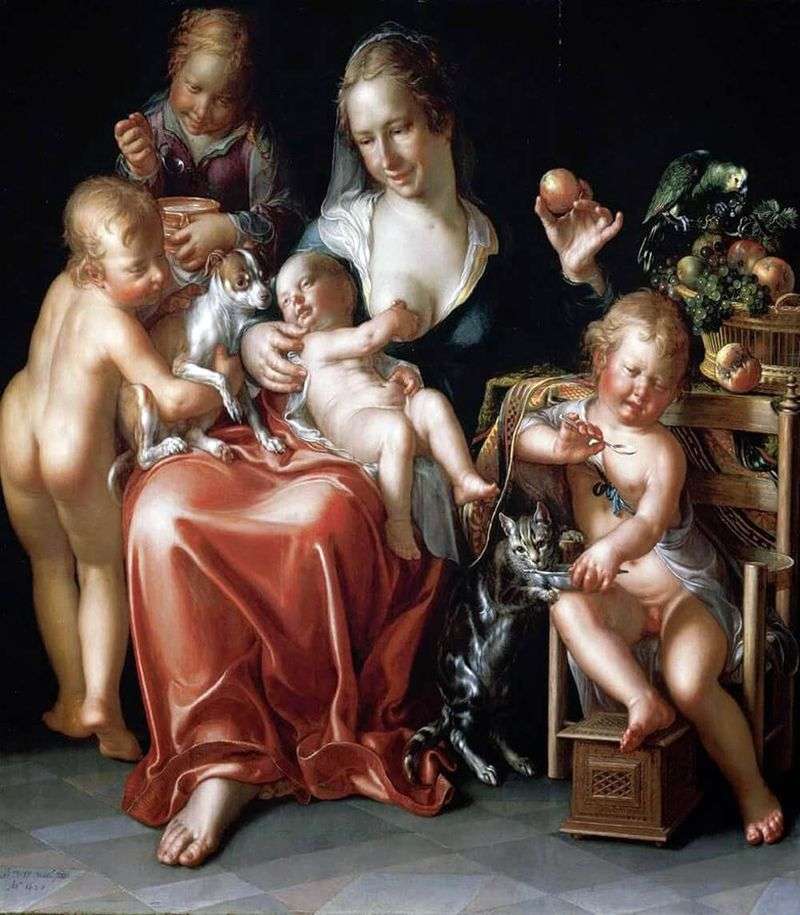

Painting by artist Joachim Eyteval “Mercy”. The size of the picture is 83 x 73 cm, canvas, oil. Charity is a property of character that determines a constant moral pattern of human actions. The content of the concept varied depending on the change in the criterion of morally good at different stages of development of the ethical consciousness of mankind.
The ancient Greeks distinguished the four basic concepts of charity: wisdom, courage, justice and moderation, tried to reduce them to one principle and, according to Socrates, saw in wisdom the highest degree of charity, which includes all others, and in the mind the source of mercy. Aristotle first distinguished the virtue of the will from the mercy of the mind. The first he called ethical and believed that they represent the middle between two extremes; the second – dianoetic – designate the right attitude of the mind to objects and to the lower virtues.
Stoics returned to the intellectualism of Socrates and in wisdom saw the highest degree of mercy, in the sage – the ideal of man. Christianity, negatively related to the intellectualism of the Greeks, saw in the will of the essence of human nature and opposed the four basic Greek concepts of mercy to the three theological: faith, hope and love.
The teachings of Thomas Aquinas number ten virtues: the three intellectual – wisdom, science and knowledge, the four basic Greek and the three above theological. In the new philosophy, the concept of freedom of the spirit and the highest good supplanted the notion of virtue and charity, as an ethical principle. Dutch painter Eytale in his painting depicted the Christian concept of charity.
 Christ and Children by Joachim Ethewal
Christ and Children by Joachim Ethewal Mars and Venus, overtaken by the gods by Joachim Ethewal
Mars and Venus, overtaken by the gods by Joachim Ethewal The Sign of the Shepherds by Joachim Ethewal
The Sign of the Shepherds by Joachim Ethewal The Evangelist Matthew by Joachim Ethewal
The Evangelist Matthew by Joachim Ethewal Miséricorde – Joachim Eiteval
Miséricorde – Joachim Eiteval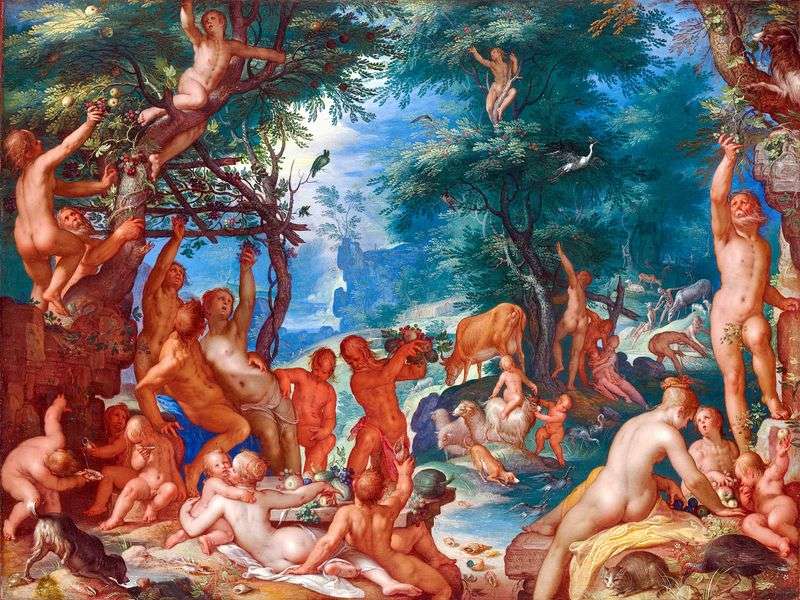 The Golden Age by Joachim Eytewal
The Golden Age by Joachim Eytewal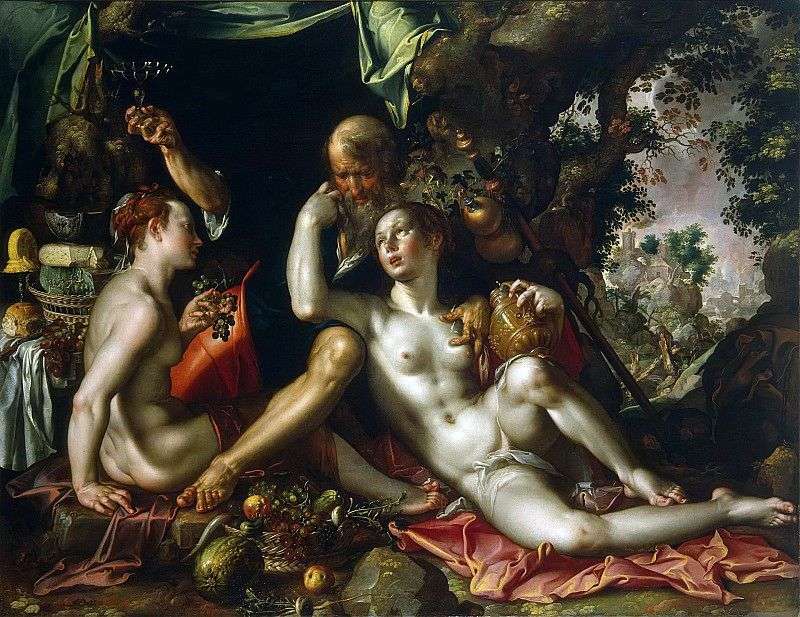 Lot and his daughters by Joachim Eteval
Lot and his daughters by Joachim Eteval Allegory of human life by Alessandro Allori
Allegory of human life by Alessandro Allori